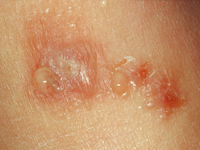
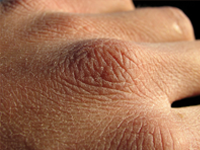
Types of Eczema
Types of Eczema
Eczema can be categorised under two main types: exogenous and endogenous.
Exogenous eczema means that it is from external causes. This includes:
- Contact Dermatitis: caused by irritants or allergies.
- Napkin Dermatitis (Nappy Eczema): caused when nappies are not changed regularly enough.
- Infective Eczema: caused by bacterial, fungal or viral infections.
- Photosensitive Eczema: caused by sun UV exposure.
Endogenous eczema means that it is from internal causes from the person’s body, or genetics.
- Atopic Dermatitis: Unknown cause, with strong genetic pattern of presentation.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: May be due to hormonal imbalance; Malassezia fungus is also strongly associated with the pustular breakouts.
- Pompholyx: Appearance of vesciles and bullae on the palms and soles of feed; unknown cause but strong associations with stress and fungal infections.
- Nummular Eczema (Discoid Eczema): Coin-shaped lesions with unknown causes.
- Pityriasis Alba: Dry, scaly, slightly whitened patches; possible in all races.
- Asteototic Eczema: Dry, cracked and fissured. Some predisposing factors include sun, wind and low humidity.
- Hypostatic Eczema (Varicose Eczema): Usually associated with varicose veins and poor venous return, where edema builds up around the area, some brownish pigmentation, and the eczema may be dry or weepy, scaly and lichenified (vertical streaks through the skin from scratching).
- Keratolysis Exfoliativa: Peeling of palms and soles with unknown causes.
- Lichen Simplex Chronicus (LSC): Damaged, thickened skin with vertical creases from over-scratching. Causes vary; treatment is to stop the ‘itch-scratch’ cycle.
- Nodular Prurigo: Nodules formed by over-scratching.